sinus lift
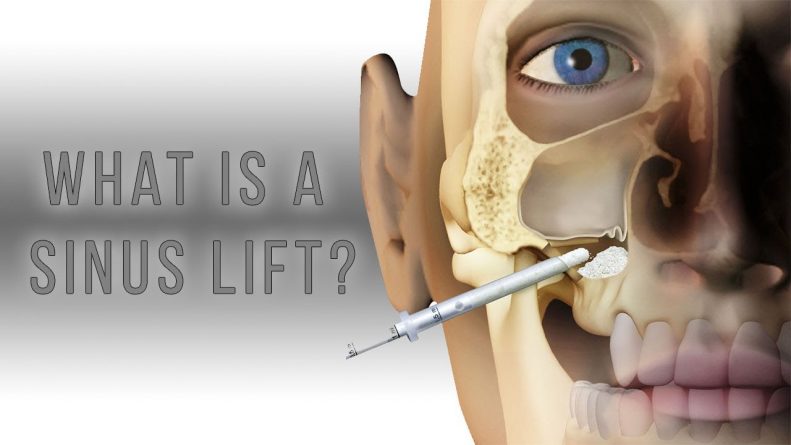 The sinus lift is a surgical procedure that is intended to increase the thickness of the jaw bone (bone of the upper jaw) at the premolars and molars, with a bone graft.
The sinus lift is a surgical procedure that is intended to increase the thickness of the jaw bone (bone of the upper jaw) at the premolars and molars, with a bone graft.
The sinus lift, also known as sinus floor elevation or sinus lift can be useful prior to a dental implant poses for strength and function of the jaw and teeth.
The price varies sinus lift surgery to perform and the practitioner, but whether in France or Tunisia the sinus lift follows the same rules and protocols.
WHAT IS A SINE LIFT?
The maxillary sinus is an air cavity in the jawbone, which often contains the roots of the premolars and molars superiors. When extracting or loss of a tooth, the bone is not as important to the body, then it is absorbed naturally and eventually atrophy. This biological process added to the air pressure contained in the bone passage can result in the lowering of the sine and a too fine bone.
The sinus lift is therefore a routine procedure, which helps strengthen the bone in order to place dental implants, while protecting the sinus floor and keeping the strength and durability required for proper operation of the jaw and teeth.
WHEN TO EXPECT SINUS LIFT?
Although there are many reasons to want to compensate for this deficiency in bone, the most common is still preparing a solid foundation for future dental implant.
The sagging of the jaw to several sources, such as:
– Loss of more than one tooth of the upper jaw (molars and premolars) for several years.
– Missing teeth due to a genetic defect
– Size and shape of the sinus unsuitable for the implant
– bone loss due to periodontitis (gum disease).
STEPS AND TECHNIQUES OF INTERVENTION
After anesthesia, the surgeon begins by cutting the gum to the place in question, and then continues according to one of two methods detailed below, previously selected with the patient.
Sinus Lift External: closed filling sinus
If there is very little remaining bone (less than 5 mm thick), a small window is opened in the side wall of the bone. Then the membrane Schneider (sinus mucosa) is detached from the bone, transplant of synthetic or natural origin is placed in the new space created between the membrane and the bone, and the gum is sutured.
The implants can be placed either after calcification, between 4 and 9 months later (this is called osseointegration process) or when the dental condition permits, the implants are placed in the same operation (protocol immediate implantation) followed by the osseointegration period.
Sinus Lift Internal: open filling sinus
If only a small filling is required and the height of the bone is sufficient (more than 6mm thick), sinus membrane is elevated and a well is created in the bone. The floored sinus is then enhanced through this well and the implant is placed in the same session if the patient’s dental situation allows (or the implant will be placed at the end of the period of calcification) , before suturing the gums.
AFTER SURGERY SINUS ELEVATION
During the days following the surgery, it is possible to bleed slightly the nose or mouth. It is important not to blow his nose to allow the graft to remain in place. Swelling of the cheek can be discerned on the 3rd day. Antibiotics and antibacterial agents are prescribed to prevent infection and pain is controllable through analgesics.
Several days after the operation, the surgeon removes the stitches (or son subside) and verifies the proper healing.
The grafted bone becomes part of the natural floored the patient’s maxillary sinus after 3 to 6 months.
SINUS LIFT IN Tunisia; The realization of a sinus lift in Tunisia unfolds similarly: international protocols are strict and respected by the dental profession overwhelmingly.
Any differences between two dentists therefore take more to the techniques used and the protocol followed that country in which it is made.
Realizing his Sinus Lift in Tunisia, like any other dental surgery, so has the same characteristics.
What are the materials used in a sinus lift?
Materials used during a Sinus Lift
Sinus Lift surgery is necessary when the loss of bone volume is too large to accommodate dental implants.
To thicken too fragile bone of the upper jaw bone filling material with specific properties are used.
THE BIOMATERIALS: ESSENTIAL TOOLS IN SINUS LIFT
A biomaterial is designed to interact with a biological system. This is the case of bone in the case of the maxillary filling. There are several categories that can be used alone or in combination:
– The autogenous bone: the patient receives a bone graft in the form of chips, from his own body. Although this involves a second surgical site (jaw, hip or leg) sampling provides excellent compatibility without immune response.
– The allogenic bone: the graft from another human individual. The sample is dried, frozen or demineralised.
– Xenotransplantation: a piece of animal bone is used. Most often used when Sinus Lift is the Bio-Oss, this bovine substitute is readily available and similar to human bone.
– Synthetic products: they contain some of the minerals contained in the bone. The alternatives are many.
– The alloplasts materials: collagen matrix is infused with growth hormones or blood cells, increasing the osteogenic potential (ability to create the bone) of the filling material.
These alternatives allow the maintenance of the membrane (high by the dentist) and good bone reconstruction.
IMPORTANT PROPERTIES OF BIOMATERIALS
Normally, bone is subject to continual renewal process, thanks to the cells that synthesize the mineral base of the bone, and others that remove old bone.
But this regeneration can not be done only when there is enough bone (resorption following tooth loss, inflammation … etc). It then fills the maxillary sinus biomaterials to assist thickening of the bone and make a solid foundation for the optimum anchoring of the dental implant.
The biological mechanism of this graft is based on three properties:
1. The osteoconduction: Cells periphery of the native bone using the material as a frame on which they can rependre and generate new bone.
2. osteoinduction: The progenitor cells are stimulated and differentiate to form bone.
3. osteogenesis: The cells from the graft directly help bone growth.
The type of filling is chosen from case to case, depending on the desired properties.
BIOMATERIALS HOW IS IT USED?
A graft (bone chips) is taken and if necessary, mixed with stimulating factors.
If animal biomaterials are used, they are sterilized at high temperatures to eliminate the risk of disease transmission and meet international standards ISO 9001 and EN 46001.
Following the sinus opening and the elevation of the membrane Schneider, the graft material is inserted into the maxillary floor. Next, a synthetic collagen membrane is positioned to protect the native membrane during the graft to prevent the filling from being dispersed. A confined space is formed, suitable for the release of development of protein.
The surgeon may choose to ask the dental implant later, after complete healing of the graft, or during the same operation following the protocol followed. All materials introduced are resorbed and replaced by native bone after 3 to 6 months. This is the period called osseointegration.

